Harvesting in the Mt. Hood National Forest: A Comprehensive Guide
The Mt. Hood National Forest is a bountiful treasure trove of natural resources, offering a diverse range of plants, mushrooms, berries, and other items for harvest. However, it is crucial to understand the limits and regulations surrounding the harvesting of these items to protect the delicate ecosystem and ensure sustainable use. In this article, we will cover the different items you can harvest from the forest, their respective limits, and some helpful tips to get you started.
Make sure to scroll to the bottom for relevant links, permits, maps, and more
Harvesting Mushrooms
Daily and annual limits
Mushroom enthusiasts can harvest up to one gallon of mushrooms per day, with an annual limit of 10 gallons. This restriction helps maintain a healthy mushroom population and promotes responsible foraging practices.
Identifying edible species
Before heading out to harvest mushrooms, it’s essential to know which species are safe to eat. Some popular edible mushrooms found in the Mt. Hood National Forest include chanterelles, oysters, lobsters, morels, and matsutakes. Be sure to familiarize yourself with these species and their toxic lookalikes to avoid any dangerous mistakes. We recommend either bringing a mushroom identification book or having an app to help you identify the different species
Tips for mushroom hunting
When searching for mushrooms, remember to follow these guidelines:
- Look for mushrooms in areas with high moisture content, such as near decaying logs and under dense tree canopies.
- Use a soft-bristle brush to gently clean the mushrooms before placing them in a breathable bag or basket.
- Avoid picking tiny or overly mature specimens to give them a chance to grow or release spores.
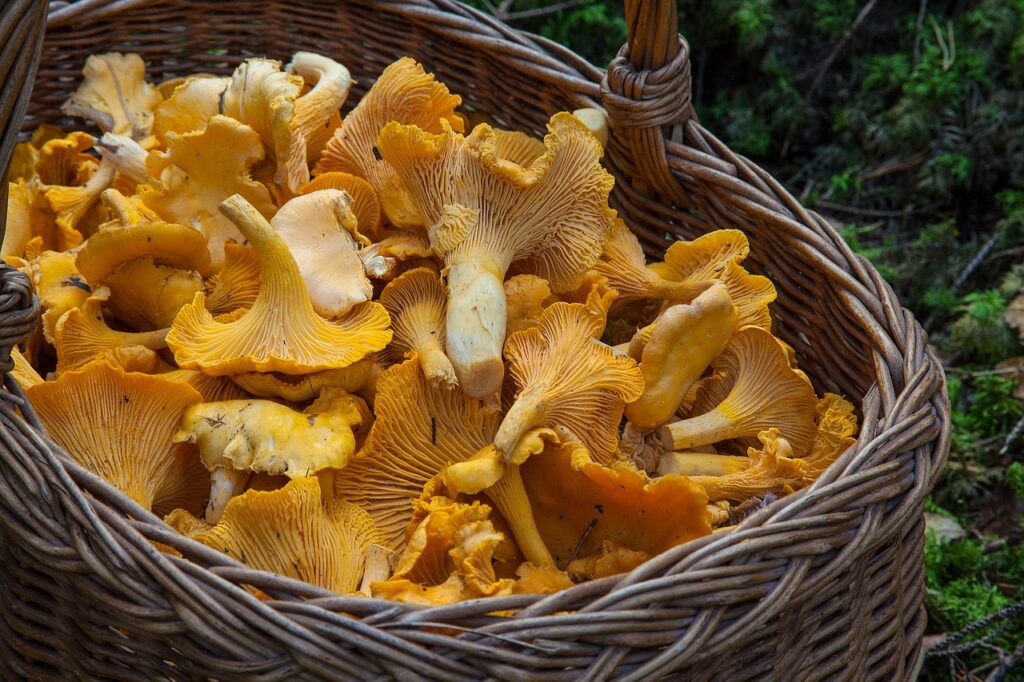


Picking Berries
Daily Limits
Berry pickers can collect up to three gallons of berries per year. This limit ensures that berry populations remain abundant for wildlife and other foragers.
Popular Berry Varities
In the Mt. Hood National Forest, you may come across a variety of berries, including huckleberries, blackberries, salmonberries, and thimbleberries. Each type of berry has its unique flavor, making them perfect for jams, pies, or simply eaten fresh.
Tips for Successful Berry Picking
To make the most of your berry-picking experience, follow these guidelines:
- Choose ripe berries that are firm, plump, and brightly colored.
- Avoid picking overripe berries, which may be mushy or moldy.
- Bring a sturdy container to hold your berries, as they can be delicate and easily crushed
Transplanting Species
Number of Transplants Allowed
Foragers are permitted to transplant up to 15 plants under 2 feet tall per year. This limit helps preserve the natural landscape and promotes responsible transplanting practices.
Species allowed for Transplanting
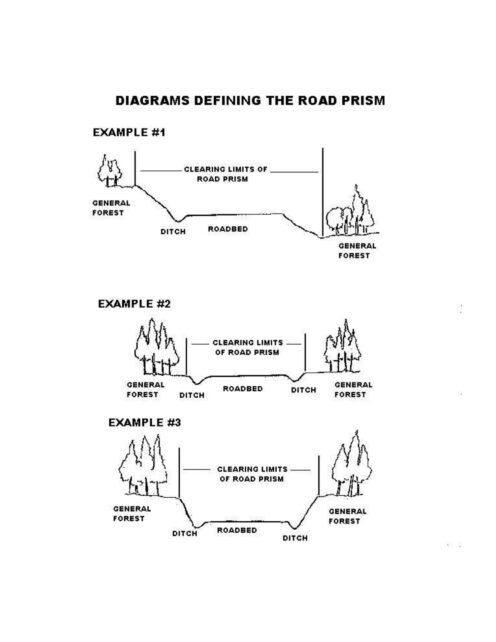
Certain species are allowed for transplanting within the road prism of open roads. These include ferns, vine maple, huckleberry, rhododendron, salal, Oregon grape, manzanita, and tree seedlings under 2 feet tall. Be sure to familiarize yourself with these species to avoid accidentally transplanting a protected plant. The road prism is the area between the roads and the general open forest, so typically the ditch and banks of the road that lead up into the forested area.
Transplanting guidelines
When transplanting plants, follow these best practices:
- Dig carefully around the root system to minimize damage.
- Prepare a suitable location in your garden before transplanting to reduce stress on the plant.
- Water the transplant thoroughly after planting and monitor it closely to ensure successful establishment.
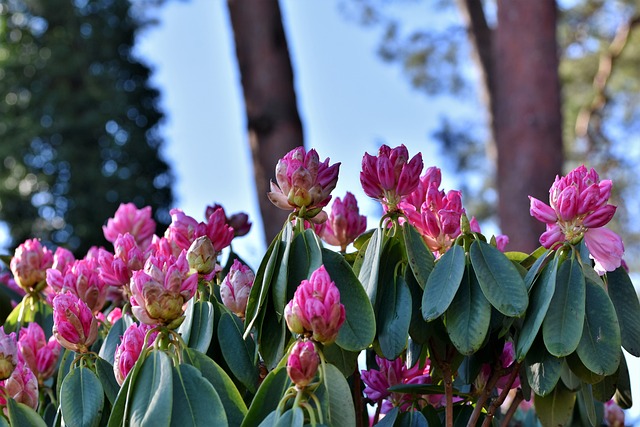

Rhododendron
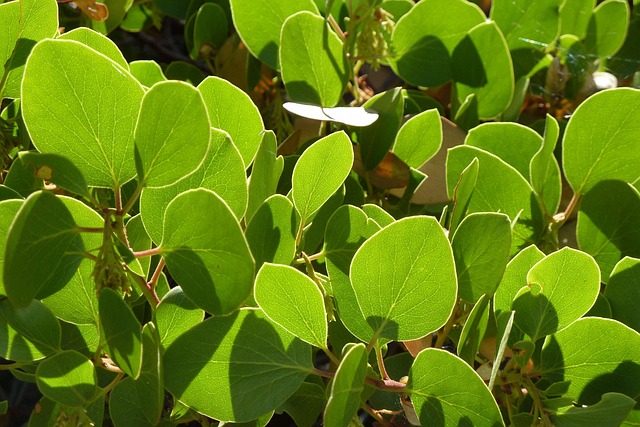

Manzanita
Collecting Cut Greenery
Amount Allowed
Up to 20 pounds of cut greenery can be harvested per year. This limit helps maintain a healthy ecosystem and ensures the availability of greenery for all. Greenery & cuttings can be harvested for up to 10 days per calendar year or until annual limit is reached.
Types of greenery Permitted
Foragers can collect greenery from the following species: ferns, vine maple, huckleberry, rhododendron, salal, Oregon grape, manzanita, bear grass, ferns, etc. These species are abundant and resilient, making them ideal for cut greenery.
Tips for cut Greenery Collection
To collect cut greenery responsibly, keep these tips in mind:
- Use clean, sharp tools to make precise cuts and minimize damage to the plant.
- Avoid taking too much greenery from a single plant to prevent overharvesting.
- Be mindful of wildlife and other plants when harvesting greenery to minimize disturbance.

Firewood
- Free use firewood permits can be requested virtually by completing & submitting the Firewood Permit Application. Permits are also available in person at your local Ranger District office. Consider calling ahead to ensure an office is open. See office hours and locations here.
- Valid government identification is required to obtain a permit.
- Personal/free use firewood permits are free of charge and expire annually when the season ends on November 30.
- Households may harvest up to 6 cords annually with a free use firewood permit for personal use only.
- Firewood harvested for resale purposes requires a Commercial Firewood Permit, which can be acquired by completing the Special Request Form (pending availability).
Christmas Trees
- Christmas Tree Permits run from Mid- November until Dec 31st
- Permit Price is $5
- Your permit allows cutting one Christmas tree up to 15 feet tall.
- Tree cutting is prohibited:
- along Hwys 26, 35, 216 and 224,
- in designated Wilderness,
- in Bull Run Watershed and The Dalles Watershed, and
- any other areas closed to public entry.
- 5 tree max per household (that means 5 permits)
- permit can be purchased at recreation.gov
Other Products
- Other harvestable products include stems, stumps and root wads, cedar products, specialty pieces and irregular logs, poles and posts, cones and seeds, boughs, and medicinals
- Each has its own protocol on how to harvest
- Do not remove products unless you are certain it is legal to do so
- Make sure to download the vehicle use maps below
Truffle Digging
Prohibition on truffle digging
When harvesting in the Mt. Hood National Forest keep in mind that truffle digging is prohibited . This restriction helps protect the delicate truffle habitat and ensures the continued availability of these valuable fungi for wildlife and future generations.
Incidental Use Vs. Commercial Permits
Definition of incidental use
Forest products obtained under “incidental use” are for personal use only and cannot be sold. This distinction ensures that the harvesting of forest products remains sustainable and does not deplete resources.
Requirements for Commecial Permits
For those interested in selling forest products, commercial permits are required. These permits help regulate the harvesting of forest products and ensure that resources are not overexploited. For more information on obtaining a commercial permit, contact your local forest service office.
For individuals who plan to sell or barter greenery or cuttings, a commercial (charge) use permit must be obtained from one of the district offices. A commercial use permit is also necessary for those who wish to collect more than the incidental use limit of 20 pounds per year. The fees, minimum purchase amounts, and regulations for different types of greenery or cuttings are outlined below.
Beargrass
has a fee of $0.05 per pound with a minimum quantity of 400 pounds. Any amount over the minimum quantity of 400 pounds must be sold in 200-pound/$10 increments, allowing one additional day to the permit for each 200 pounds. One cubic foot is approximately 12 pounds. Fronds must be pulled by hand; no tools are authorized for use in beargrass harvest. Root disturbance is prohibited.
Salal
has a fee of $0.05 per pound with a minimum quantity of 400 pounds. There are approximately 100 pounds in 75 bunches. No permits are issued for salal from July 1 – August 20.
Fern Cuttings
have a fee of $0.05 per pound with a minimum quantity of 400 pounds. Approximately 100 pounds are equivalent to 75 bunches.
Fern Clumps
have a fee of $1 per plant with a minimum quantity of 20 plants.
Others
Other cut greenery has a fee of $0.05 per pound with a minimum quantity of 400 pounds. The greenery must not exceed 1 inch in diameter and 24 inches in length. A Special Request Form must be submitted and approved before a commercial permit can be issued for any other types of cut greenery.
Please remember that these fees and regulations are subject to change. Always consult with your local district office for the most up-to-date information before harvesting any greenery or cuttings.
Restricted areas
Harvest is prohibited:
- in Tilly Jane Proposed Wilderness, Camp Baldwin area, designated wilderness, protection areas, research natural areas, municipal watersheds, heritage or administrative sites, recreation sites, riparian areas, streams, ponds, reservoirs, lakes, or wetlands unless the product occurs within a road prism open to motor vehicle use.
- along Highways 26, 35, 216 & 224; Forest Road 42 (Skyline Road); Forest Road 50 (Timberline Road); Forest Road 2645 (Westleg Road); and Forest Road 18 (Lolo Pass Road
- outside of the road prism ( see diagram)
- along ponds, rivers, and wetlands unless those fall within the road prism